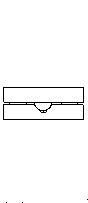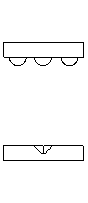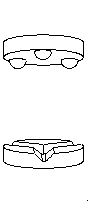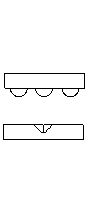
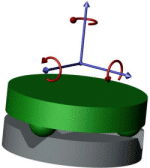
| What are they? | A kinematic coupling is a device used to repeatably position components often with sub-micron repeatability. A traditional kinematic coupling consists of three "sphere" shaped members mounted to one component and three corresponding "v-shaped" grooves attached to, or machined into the other component. |
Traditional Kinematic Coupling |
| How they work. | To deterministically locate two components, 6 relative degrees of freedom (3 translation & 3 rotation) must be constrained. To do so, exactly 6 points of contact between the two components are needed. In a traditional kinematic coupling, this is accomplished through 2 points of contact at each sphere - groove joint. |
6 Relative DOF |
| Performance | It is difficult to give a concrete number for the repeatability of
a kinematic coupling as this is dependant upon many factors:
However, the repeatability of kinematic couplings has been measured as low as 0.02 microns. This is less than the wavelength of visible light! |
|
| Applications | Kinematic couplings can be used in most applications which require
repeatable location. Examples include:
|